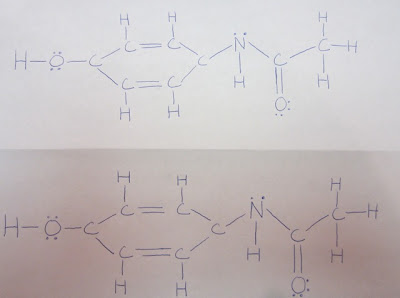
Intermolecular Forces that Act Upon a Pair of Acetaminophen Molecules
Three forces act on pairs of Acetaminophen. These forces are Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole Dipole, and London Dispersion. Hydrogen bonding acts on a pair of Acetaminophen molecules because the Hydrogen in one of the molecules bonds with the Oxygen in the other. This creates a powerful force that is difficult to break. Dipole Dipole forces act upon a pair of Acetaminophen molecules because both Acetaminophen molecules are polar. This force is slightly weaker than Hydrogen Bonding. Finally, London Dispersion Forces also act on a pair of Acetaminophen molecules. London Dispersion Forces act upon all molecules. “The London Dispersion force is a temporary attractive force that results when the electrons in two adjacent atoms occupy positions that make the atoms form temporary dipoles.” (Purdue Chemistry Lab) Because electrons are moving at all times, there will always be London Dispersion Forces present between all molecules, including Acetaminophen.
No comments:
Post a Comment